Taking Care of Your Hearing Aids
If you take good care of your hearing aids, your hearing aids should take
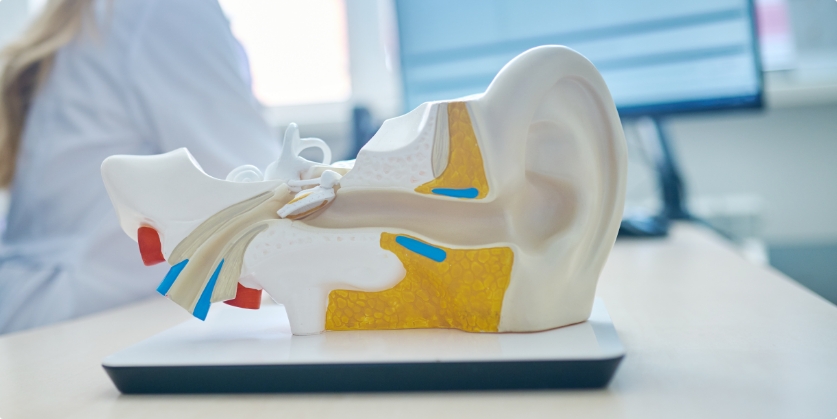

If you take good care of your hearing aids, your hearing aids should take

One of the questions that people often ask us as audiologists is, “when

The holiday season is here and many of us will be traveling to